Life Expectancy by Income: Exploring the Link Between Wealth and Health
**What is the link between income and life expectancy?**
Life expectancy is often seen as a key measure of a population’s overall health and well-being. It is influenced by a multitude of factors, including genetics, lifestyle choices, and access to healthcare. However, recent studies have shown that income plays a significant role in determining life expectancy.
**The Impact of Income on Health**
Income inequality has long been a topic of concern in society. But beyond the economic implications, research has increasingly pointed to its detrimental effects on health. The relationship between income and life expectancy is not a simple one, but multiple studies have consistently shown a correlation between higher income and longer life expectancy.
**The Income-Health Gradient**
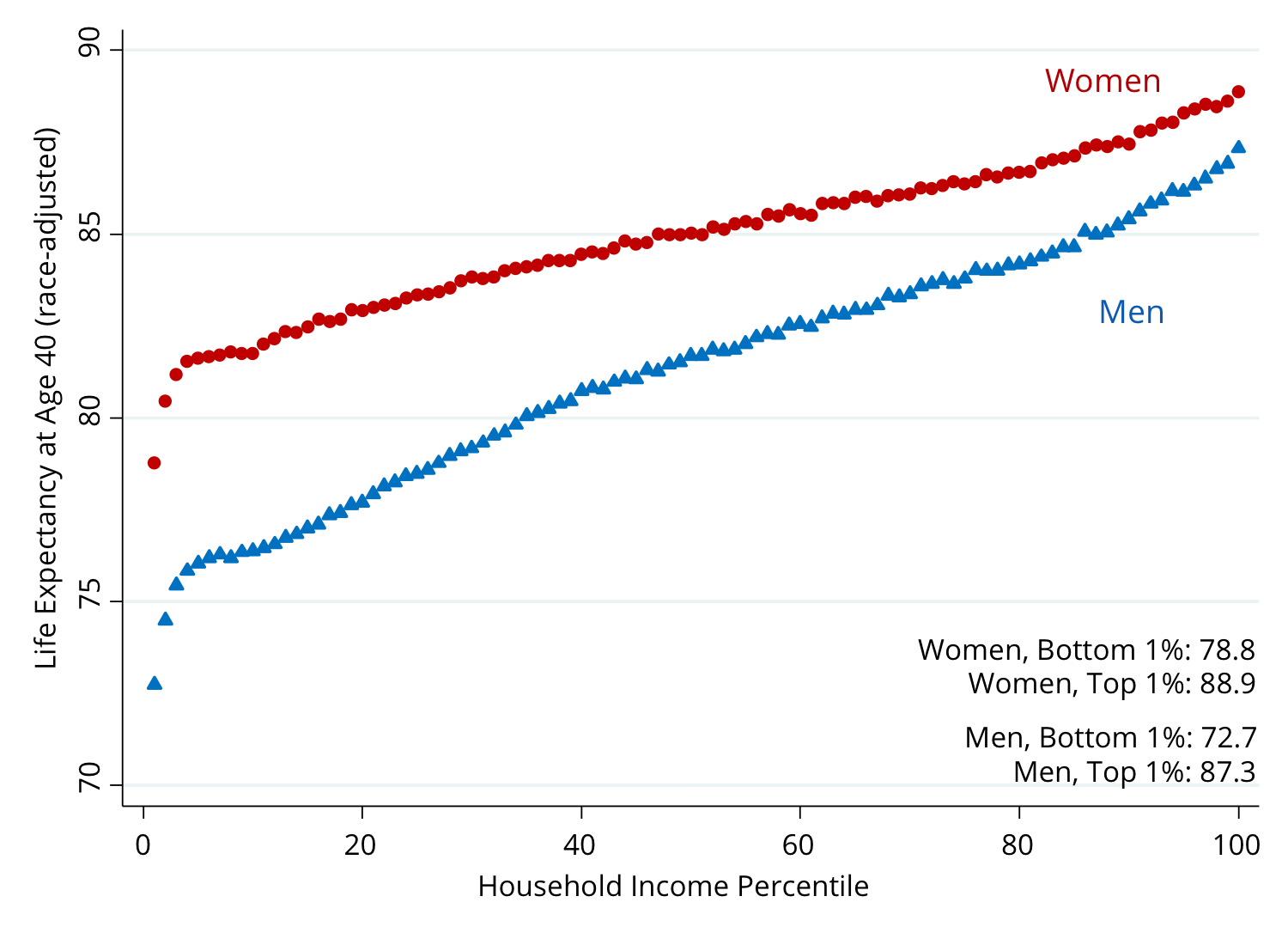
Researchers have observed a clear pattern in which individuals in higher income brackets tend to have better health outcomes and longer lives compared to those in lower income brackets. This pattern, known as the income-health gradient, holds true across countries and spans various measures of health, from overall life expectancy to disease-specific mortality rates.
**Exploring the Factors**
Several factors may contribute to the connection between income and life expectancy. Let’s delve into some key aspects that shed light on this relationship.
1. **Access to Healthcare**: Individuals with higher incomes often have better access to quality healthcare, including preventive services, regular check-ups, and early disease detection. This leads to better management and treatment of health conditions, ultimately impacting life expectancy.
2. **Education and Knowledge**: Higher income levels are typically associated with higher levels of education and knowledge. Well-educated individuals are more likely to make informed health choices, adopt healthier behaviors, and seek timely medical care, all of which can significantly impact life expectancy.
3. **Living Conditions**: Income affects living conditions, such as housing quality, access to clean water and sanitation, and exposure to environmental hazards. These factors can have a substantial impact on health outcomes and overall well-being.
4. **Nutrition**: Higher income allows individuals to afford a more nutritious diet, which is vital for maintaining good health and preventing chronic diseases. Adequate nutrition plays a critical role in a person’s immune system, cognitive development, and overall resilience against diseases.
5. **Stress and Mental Health**: Financial stability and security positively influence mental health, reducing stress and anxiety. Chronic stress and mental health disorders have been linked to a range of negative health outcomes, including a shorter life expectancy.
**Understanding the Mechanisms**
While these factors provide insights into the connection between income and life expectancy, it’s essential to understand the underlying mechanisms that drive these associations.
1. **Income Inequality**: High levels of income inequality within a society can lead to disparities in access to resources, opportunities, and healthcare. These gaps contribute significantly to variations in life expectancy between different income groups.
2. **Social Determinants of Health**: Income is a social determinant of health, meaning that it impacts health outcomes not only through individual choices and behaviors but also via systemic and structural factors. Addressing the social determinants of health is crucial for achieving health equity and reducing income-based health disparities.
3. **Cumulative Disadvantage**: The cumulative disadvantage theory suggests that individuals with lower incomes face a cumulative burden of adverse circumstances throughout their lives, including limited access to healthcare, higher exposure to environmental risks, and limited educational and employment opportunities. These accumulated disadvantages can have long-term effects on health outcomes.
4. **Intergenerational Effects**: The impact of income on health extends beyond individual lifespans. A person’s socioeconomic status, including their income, can influence the health and well-being of future generations. This suggests that policies aimed at reducing income-based health disparities can have intergenerational benefits.
**Frequently Asked Questions**
**Q: Is the income-health gradient observed in all countries?**
Yes, the income-health gradient has been observed across countries with varying levels of income inequality. However, the extent of the association may vary depending on factors such as the strength of social safety nets, access to healthcare, and overall socioeconomic development.
**Q: Can improving income equality improve life expectancy?**
Addressing income inequality can contribute to improved life expectancy, as it helps create more equitable access to healthcare, education, and other resources. Policies focused on reducing income disparities and providing support for disadvantaged populations have the potential to positively impact health outcomes.
**Q: Does the income-health gradient exist within income brackets?**
While the income-health gradient is most evident when comparing extreme income groups, such as the wealthy and the poor, it does exist within income brackets as well. Even relatively small differences in income can have significant effects on health outcomes and life expectancy.
**Final Thoughts**
The link between income and life expectancy is a complex and multifaceted issue. As research continues to shed light on the connections and mechanisms, it becomes increasingly clear that addressing income-based health disparities is crucial for achieving health equity and improving overall population health. By implementing policies and interventions that promote income equality and provide equal access to healthcare and resources, societies can strive towards a future where everyone has an equal opportunity to live a long and healthy life.